In a fascinating discovery made by Hubspot in 2021, it was reported that Google processes approximately 63,000 search queries every second.
You must be wondering then, what exactly are people looking for on Google that makes them use the platform this much.
Well, that depends on who you ask.
Some people use the search engine to get information, some use it to get an education, some use it to validate their points while arguing (I do that a lot), and there are those who use it for product research (e.g., is company XYZ legit).
Now, in order to ensure your pages are what these searchers see when they come to use Google, you have to get your SEO rig properly oiled.
Clearly, there are a number of ways to do that. But for the scope of this post, we’re going to explore the content angle of that. That is, creating content that helps your SEO goals.
What are SEO contents?
SEO contents are contents you create for the sole purpose of ranking on the SERP. On the surface, that statement sounds like creating content to satisfy the search engine algorithms. But people in the SEO world know that an attempt to satisfy search engine algorithms is also an effort to please human users.
So, technically, we’re saying that SEO contents are contents you create to rank on the SERP and meet the needs of searchers.
Generally speaking, there are many of such contents around today. But for this post, we’ll only be looking at the best ones – i.e., SEO content that is known to yield the best results.
- Blog content
Blogs are some of the most popular pieces of content on the internet today. According to various sources, about 7 million blog posts are published per day.
Wow. That’s so huge.
Indeed, blog posts rank at #1 on this list for the sole reason of their popularity. Virtually all Google search result pages feature at least one blog post,
The reason for this popularity is because blog posts are easy to read and digest for readers, they’re short and straight-to-the-point, they make for quick communication of opinions. And from a business or site owner’s perspective, blog posts are quite SEO-friendly, which is thanks to the ease of inserting keywords in them. A simple blog post – if written well – can be used to target a certain keyword. And that will, in turn, help a business rank above its competitors and win some more sales.
What do blog posts look like? Someone quips. Short, 500-1000 words, five minutes read, concise articles on the internet. Rings a bell? Maybe not.
Anyways, blog posts can take any of the following forms.
- List-type blog posts. E.g., 7 ways to paint a room, 5 unique ways to ask a girl out, 5 types of engagement rings, etc.
- How-To Guides. E.g., How to decorate a small room, how to pay off your debt, how-to DIY your dislocated arm, etc.
- Checklists/Cheat Sheets. Useful tool that helps users check items off a list
- Infographics. Great visuals FOR providing quality information in image forms.
- Interviews. Awesome piece of content that showcases authority and expertise. Can drive more authentic traffic to a website.
- Newsworthy Articles. E.g., press releases, PR content, product reviews, etc.
- Personal Stories. E.g., real-life testimonials, reports, etc.
How to use Blog Posts for SEO
- Use one or two long-tail keywords
- Add images, but don’t forget to attach the image alt text
- Optimize blog posts for mobile devices
- Litter blog posts with LSI keywords
- Link to related content online
- Use primary keyword in the meta description
- Try as much as possible to format blog post so that it passes for a snippet
- Guest Posts
Guest posts are the twins of blog posts. They carry all the elements of blog posts and can even take any of the blog post forms earlier listed.
However, the big difference between blog posts and guest posts is that the latter is usually published on someone else’s web platform.
For example, say your site name is XYZ.com. Guest blogging involves creating a blog post for your site (XYZ.com) and then publishing it on another site named ABC.com.
You must be wondering, why contribute a piece on someone else’s website when you can easily publish it on yours?
If 3% of all blogs on the internet are doing something – publishing over 100 guest posts per month – don’t you think there has to be a reason?
The first is for the PR. Publishing a post on someone else’s blog and then stating your blog name as the source is a straight route to brand PR. With that, the audience on this other site can easily see your brand name and check your site out as a result.
The second reason is the backlink. Backlinks are a crucial part of SEO. According to the Moz blog, “Backlinks are especially valuable for SEO because they represent a “vote of confidence” from one site to another.” Indeed, getting a backlink from a site to yours is a great way of boosting your site’s SEO. But before someone can give you a backlink, you, too, must have given something in return – guest post, in this case.
How to use guest posts for SEO
- Find the Top-ranking Blogs in your niche
- Produce a mind-blowing blog content
- Follow the 7-step process for optimizing blog posts as described in #1 above
- Create a type of content that will wow the readers of your target blogs
- Use the right anchor text while attaching your site link in guest posts
- Long-form Content
Long-form content is the stack opposite of blog posts. Whereas the latter focused on short, concise content, long-form content advocates for longer, in-depth analyses of concepts.
The idea of long-form content became popular when Google started prioritizing long and expansive blogs on their SERPs. It’s believed that the reason for this change is because of the sudden interest in in-depth content by readers.
Nowadays, readers are happy to read a 10k+ word long article so long as the article helps them achieve their aim. Put simply; it’s no longer a function of how long an article is, but rather how effective.
Another beautiful thing about long-form content for SEO is that it allows you to use your primary keywords and its LSI family richly. In fact, you can cover any number of keywords you need to.
While traditional short-form blogs may allow you to use a keyword only three times, long-forms can take the numbers up to like seven or ten without you appearing like you’re practicing keyword stuffing.
Finally, Google likes long-form content, which is great news from an SEO perspective. A while back, a company called SerpIQ did a quick study featuring the top 10 results on a SERP. They compared these results by content length and discovered that the first result typically has 2,416 words and the 10th result has 2,032 words.
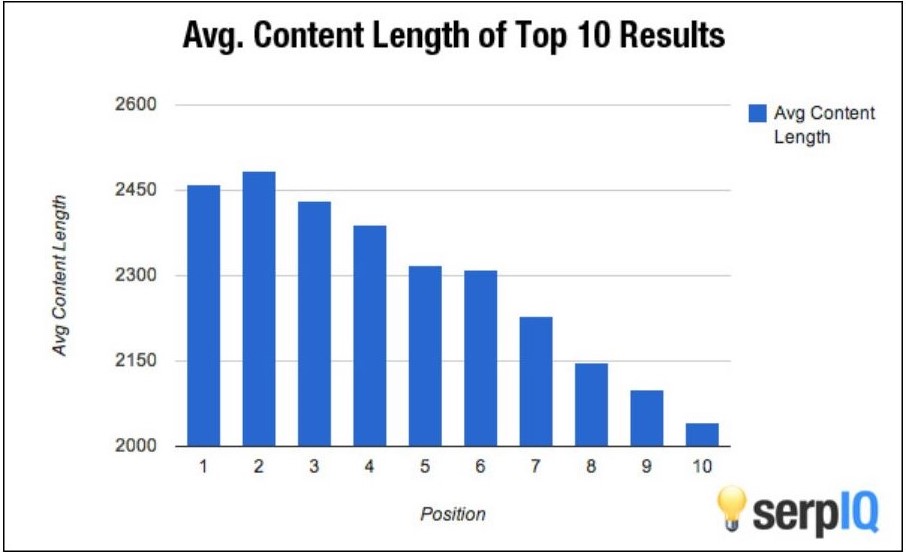
That tells you immediately where Google’s interests lie. Start creating long-form content today. It’s good for SEO.
- Data-focused content
Often, people come to Google to search for statistics, data, research figures, and facts. Some of these are marketers, webmasters, business owners, SEO consultants, and regular internet users.
Because of the love for these types of content and also because of their data-focused nature, Google prioritizes these contents on the SERPs.
That’s why when you search for things on Google, you’ll likely see results with percentages, stats, or figures first before you see others.
The belief is that stats-based content showcases expertise, authority, and trustworthiness (E-A-T). And since Google is obliged to deliver the best results to its searchers, presenting these kinds of results first makes the best sense.
How to use data-focused content for SEO
- Mix with blog content. Data-focused content shouldn’t exist alone. Instead, use it to improve regular blog content quality. An article about COVID, fashion, or staff recruitment will likely do better on the SERPs if it has data-backed facts embedded in it.
- Keep the stats, facts, or figures close to the main keywords
- If possible, mention the existence of data in the content title. E.g., How to eliminate wrinkles permanently (science-backed findings).
- Case studies
Another type of content you’ll likely find on Google SERPs is case studies. This type of content can help to show how a specific solution solves a problem, how a certain product works, or areas of applications of certain concepts.
Often, people look for case studies when they’re confused or don’t understand the true limits of a product. Or when they need to understand the benefits of an offering – i.e., what the product can do.
For example, someone may come to Google to search for case studies of HIV cure or case studies of how a popular gaming patchworks.
In short, there can be case studies for almost anything.
How do case studies help with SEO?
Case studies help with SEO from the search intent angle. Normally, it’s believed that every searcher has an intention for coming to Google – to learn, get entertained, be informed, to research, etc.
Now, when someone searches for something that demands a case study kind of result, Google tries to understand their intent and then display results that match their query.
If you’ve published case study content that addresses the problem people are searching for a solution to, your page will definitely be amongst the results.
A hypothetical case
Imagine you offer aromatherapy as a service. Then you create many case studies of aromatherapy helping people – whether in the form of video, before or after picture proof, or regular blog content.
Now, when someone comes to Google to search for a query like, “Does aromatherapy really work?” Google will understand the intent of this searcher – that he/she wants proof of the effectiveness of aromatherapy – and then display some or one of your case studies to show them that, indeed, the method works.
- Infographics and visual content
From an SEO perspective, visual content doesn’t usually get much attention. Largely because Google can’t read images. As such, creating standalone memes, images, and infographics might seem like a waste of time from an SEO angle.
So, does that mean visual contents are completely useless in the SEO space? Far from it.
When you search for something on Google, the result page is usually displayed with separate frames for ‘All,’ ‘Images,’ ‘Videos,’ ‘Maps,’ ‘News,’ ‘Books,’ etc.
Under the image, the tab is where you’ll find those images, memes, and infographics Google has extracted from relevant web pages.
See an example:
If your images manage to make it to this page, that’s a win already from an SEO perspective. The question then is: what’s the criterion for having your visuals displayed on this tab?
Here’s what Google has to say about that, “To include a picture in Google search results, add your image to a website along with a description. While you can’t directly upload images into search results, searchable images posted on a website can show up in our search results.”
From that statement, what we can deduce is that to make your images appear in the search results, you need to:
- Use image alt text (for image description)
- Properly name the image file on your web page
- Optimize the image for SEO (size reduction, resolution adjustment, etc.)
- Make sure the image is relevant to the context of the web page
Besides all these, another important metric that can help your images make it into the search results is social and link signals.
Normally, when an infographic, meme, or image is captivating, people may share it with their friends and followers. As soon as the number of shares becomes noticeable, search engines may become alerted, known as a social signal.
Furthermore, to share with friends and followers, some people may choose to share the image link rather than a screenshot. When they do this, they’re indirectly sending a backlink to the real image source. These are called link signals.
As you might have guessed, both social and link signals are important ranking factors irrespective of where they’re coming from.
- Tool-based content
Tool-based content refers to items such as calculators, templates, generators, converters, checklists, etc. Usually, people come to Google to search for these types of content when they need help with something.
For example, someone who wants to calculate his/her mortgage rate may come to Google to search for a mortgage calculator. If you’ve created this tool, Google may include you in the list of calculators on the results page.
Furthermore, creating tool-based content can also lead to free backlink generation. How? You wonder.
Many site owners may include this tool in their web content if it benefits their audience when you create a tool. However, doing that means they have to give credit (backlink) to you.

